Which of the Following Mechanisms of Change in Gene Frequencies
Two of the most relevant mechanisms of evolutionary change are. If new individuals immigrate into a population then the frequency will change.
Natural selection natural selection.

. Which of the following mechanisms of change in gene frequencies is responsible for the antibiotic resistance of E. Population genetics is the field of biology that studies allele frequencies in populations and how they change over time. Microevolution is a change in the frequency of gene variants alleles in a population typically occurring over a relatively short time period.
When one or more of these forces are acting in a. No selection can occur so that certain alleles are not selected for or against. Describes mutation natural selection in several aspects gene flow and genetic drift SlideShare uses cookies to improve functionality and performance and to provide you with relevant advertising.
Imagine that you observe an increase in the frequency of brown coloration genes and a decrease in the frequency of green coloration genes in a beetle population. Allele frequency refers to how common an allele is in a population. Which of the following mechanisms of change in genefrequencies is responsible for the antibiotic resistance of E.
Which of the following mechanisms of change in gene frequencies is responsible for the antibiotic resistance of E. Migration occurs when a large influx of people moves into another population and interbreeds with the latter. Gene flow within the population is less than gene flow between populations.
Mutation genetic drift natural selection and gene flow. Natural Selection Connect Saved Help Save Exit Submit Changes in gene frequency Which of the following mechanisms of change in gene frequencies is responsible for the antibiotic resistance of E. In the end gene frequency can be regulated by such mechanisms as natural selection sexual selection genetic drift gene flow and mutation.
There are four key mechanisms that allow a population a group of interacting organisms of a single species to exhibit a change in allele frequency from one generation to the next. Coli in this experiment. Genetic drift genetic drift.
Which of the following mechanisms of change in gene frequencies is responsible for the antibiotic resistance of Ecoli. Mutation migration genetic drift and natural selection are all processes that can directly affect gene frequencies in a population. Gene flow gene flow.
Random mating must occur ie. Those factors are natural selection mutation genetic drift and migration gene flow. - natural selection - founder effect - population bottleneck - genetic drift.
Coli in this experiment. No gene flow can occur ie. Reproduction is non-random within the population.
These are evolution by. Four major forces are usually listed for changing gene frequencies in populations namely migration mutation selection and random genetic drift. If you continue browsing the site you.
Multiple Choice O population bottleneck founder effect natural. Biol 3 Summer 2020 Fall 2020 Status Update Reedley. There are a few basic ways in which microevolutionary change happens.
Coli in this experiment. Which of the following mechanisms of change in gene frequencies is responsible for the antibiotic resistance of E. Allele frequencies in a population may change due to four fundamental forces of evolution.
However natural selection and genetic drift can only change the frequency of different genes and genetic elements eg making wide beaks or green beetles more or less common. Which of the following mechanisms change in gene frequencies. Natural Selection Genetic Drift Mutations and Gene Flow.
If a new gene is added through mutation it can affect the frequency. If a gene mutation in a population of Firebeards and Ironfists created a new type of Dwarf the Stiffbeards then obviously the frequencies in the gene pool will change. Mutations are the ultimate source of new alleles in a gene pool.
Natural selection genetic drift and gene flow are the mechanisms that cause changes in allele frequencies over time. Individuals must pair by chance The population must be large so that no genetic drift random chance can cause the allele frequencies to change. In order to bring about the change of the gene frequency in a population natural selection depends on the interplay of the intrinsic and extrinsic factors Xu 2010.
Gene flow can cause new alleles to enter a populations gene pool. The Pointer Finger- Gene Flow. Of the ways that populations can evolve over time is the only mechanism in which the environment selects for better adapted individuals whereas selects traits by random chance.
Natural selection genetic drift and gene flow are the mechanisms that cause changes in allele frequencies over time. Natural Selection and Genetic Drift. In fact we know they are probably always affecting populations.
Natural selection Two agar plates one containing the antibiotic streptomycin and one without antibiotics are inoculated with E. The Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium principle says that allele frequencies in a population will remain constant in the absence of the four factors that could change them. Mutations introduce new alleles into a population.
Genetic drift results in a change in gene frequencies because. These forces constitute the mechanisms underlying the evolutionary process. Gene pool frequencies do not change as a result of migration in or out of a population.
Natural selection works by selecting alleles that confer beneficial traits or behaviour. No migration of individuals into or out of the population. Gene flow occurs only as a result of isolation of a small population.
Coli in this experiment. All of these mechanisms can cause changes in the frequencies of genes and other genetic elements in populations and so all of them are mechanisms of evolutionary change. When one or more of these forces are acting in a population the population violates the Hardy-Weinberg assumptions and evolution occurs.
Coli in this experiment.

Migration Natural Selection Genetic Drift Evolution

Microevolution Is The Change In Genetic Frequency Of An Allele In A Given Population This Change Arises Evolutionary Biology Biology Teacher Science Education

Best Nootropic Choline Supplement Source Citicoline Alpha Gpc Or Choline Bitartrate Nootropics Alpha Gpc Choline Supplement
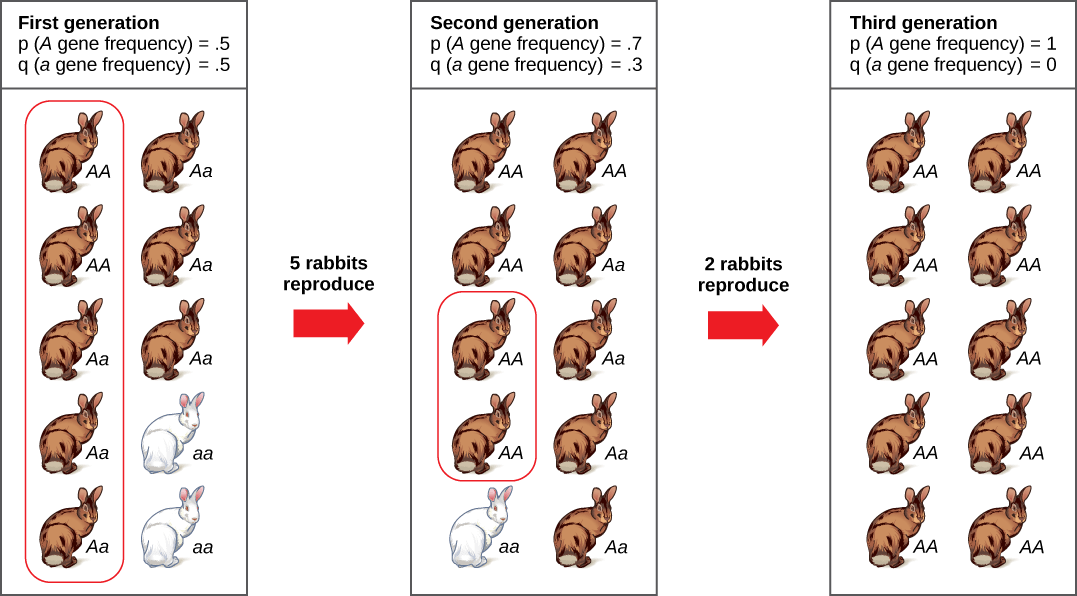
Other Mechanisms Of Evolution Biological Principles

Bottleneck Effect Genetic Drift Genetics Science Biology

Gene Flow Understanding Evolution

Evolution Concept Map Evolution Concept Map Concept Map Biology Lessons

Natural Selection Darwin S Theory Of Evolution Evolution Biology Units

Anything But Ordinary Emerging Splicing Mechanisms In Eukaryotic Gene Regulation Trends In Genetics

Migration The Movement Of Alleles Between Populations Means Gene Flow Transfer Of Alleles From Gene Pool To Gene Pool Mechanisms Ran Evolution Biology Flow

The Hardy Weinberg Principle Learn Science At Scitable

Evolution Concept Map Evolution Concept Map Concept Map Biology Lessons

Pin By Mary Margaret Barbee On My Notes Biology Notes Text Features Worksheet Kindergarten Worksheets Printable

Isolating Mechanisms Definition Examples Expii

Role Of Transposons In Evolution Genetic Education Non Replicative Mechanism Of Transposition Evolution Genetic Sequence Gene Expression





Comments
Post a Comment